Dental fluorosis
What Is Dental Fluorosis?
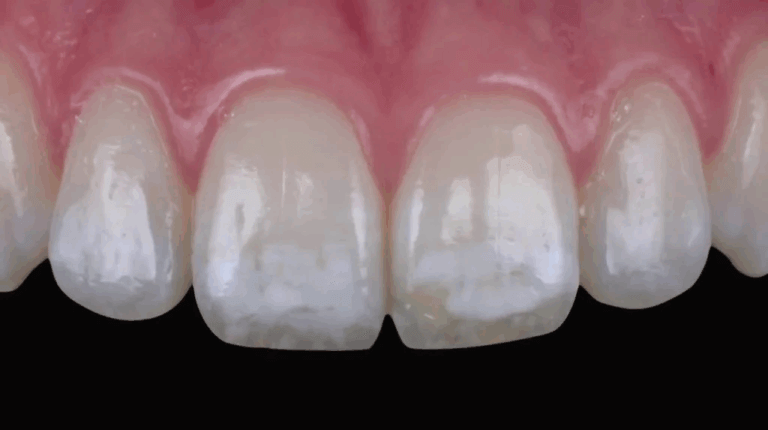
Dental fluorosis is a cosmetic dental condition caused by overexposure to fluoride during the early years of tooth development. It can affect the appearance of teeth, causing discoloration and surface irregularities. Understanding its causes, signs, and treatment options is essential for maintaining optimal oral health and an attractive smile.
Before you contact a Toronto dentist to examine dental fluorosis, there are some things you should know as a patient:
- Types of Dental Fluorosis
- Causes of Dental Fluorosis
- Signs And Symptoms Of Dental Fluorosis
- Treatment Options For Dental Fluorosis
- Managing Dental Fluorosis Until You Can See A Dentist
- Frequently Asked Questions About Dental Fluorosis
If you have questions about Dental Fluorosis or other dental problems, please contact us for more information.
Types of Dental Fluorosis
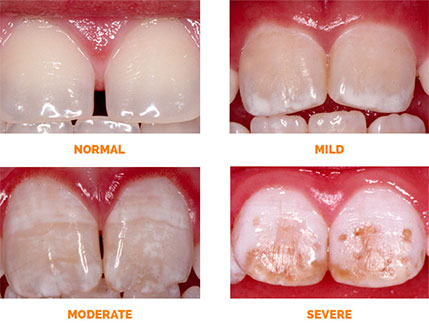
Dental fluorosis is generally classified based on severity:
- Questionable or Very Mild: Barely noticeable white spots.
- Mild: Small white areas covering less than 25% of the tooth surface.
- Moderate: White spots cover more of the tooth and may include some brown staining.
- Severe: Widespread discoloration, brown stains, and enamel pitting or surface irregularities.
Identifying the severity of fluorosis is key to determining the most suitable cosmetic treatment. For more information about how to treat your specific case of Dental Fluorosis, please contact us.
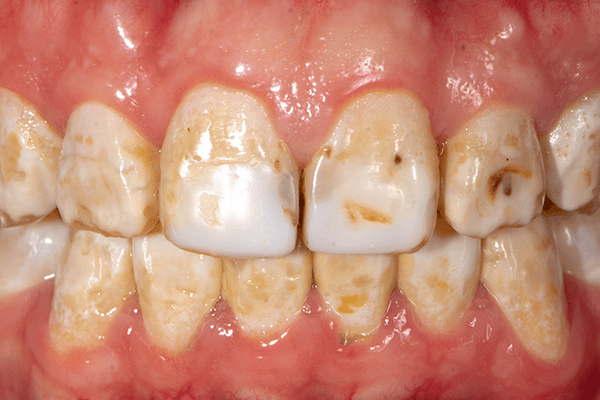
Causes of Dental Fluorosis
Dental fluorosis occurs when children ingest too much fluoride while their teeth are developing (typically under the age of 8). Common causes include:
- High Fluoride Levels in Drinking Water: Excess fluoride in natural or municipal water supplies.
- Swallowing Fluoridated Toothpaste: Young children may accidentally ingest toothpaste during brushing.
- Excessive Use of Fluoride Supplements: Overuse of fluoride tablets or drops without dental supervision.
- Fluoride in Infant Formula: Using fluoridated water to mix formula can contribute to excess fluoride intake.
Understanding and managing fluoride exposure during childhood is essential to prevent dental fluorosis. If you have further questions about Dental Fluorosis and how to treat it, please contact us.
Signs and Symptoms of Dental Fluorosis
The appearance of dental fluorosis can vary from mild to severe, depending on the level of fluoride exposure. Key signs include:
- White Spots or Streaks: Chalky white marks, typically on the front teeth.
- Brown or Yellow Discoloration: In moderate to severe cases, teeth may appear stained or mottled.
- Surface Irregularities: Severe fluorosis can cause pitting or rough enamel surfaces.
- Resistance to Staining: Ironically, while discoloration is present, affected teeth may be more resistant to cavities.
Early detection of these signs can guide appropriate treatment to restore your smile’s aesthetics. If you have further questions about the signs and symptoms of Dental Fluorosis, please contact us.
Treatment Options for Dental Fluorosis
Treatment depends on the severity of fluorosis and your aesthetic goals:
- Icon Resin Infiltration: A minimally invasive treatment that can penetrate and mask white spots or mild fluorosis discoloration without drilling or removing healthy enamel.
- Dental Veneers: Custom porcelain shells are bonded to the front surface of teeth, concealing moderate to severe fluorosis stains and restoring natural appearance.
- Dental Bonding: Composite resin is applied to cover and blend in discolorations, ideal for moderate cases of fluorosis.
- Dental Crowns: For severe fluorosis with significant enamel damage, full-coverage crowns can strengthen and protect the tooth while improving aesthetics.
Your dentist can help select the right treatment to enhance both the health and appearance of your smile. For more information about Dental Fluorosis treatment, please contact us.
Managing Dental Fluorosis Until You Can See the Dentist
If you notice signs of dental fluorosis in your child’s teeth:
- Limit Fluoride Exposure: Use fluoride toothpaste sparingly and avoid swallowing.
- Monitor Water Sources: If using well water or municipal water with high fluoride levels, consult your dentist or local health department.
- Good Oral Hygiene: Maintain daily brushing and flossing to keep teeth clean and minimize additional staining.
- Schedule a Dental Evaluation: Early diagnosis and intervention can help prevent the need for more extensive treatments.
Taking proactive steps at home can help prevent further discoloration and protect your oral health until professional care is provided. If you have further questions about Dental Fluorosis, please contact us.
Frequently Asked Questions About Dental Fluorosis
- Can dental fluorosis be reversed?
No, fluorosis is permanent once teeth are formed. However, cosmetic treatments like whitening or veneers can improve appearance.
- Does fluorosis affect permanent teeth?
Yes, but only if excess fluoride exposure occurs during tooth development (usually under age 8).
- Is dental fluorosis harmful to oral health?
In most cases, it’s a cosmetic issue. However, severe fluorosis with enamel damage may increase risk for wear or cavities.
- Can adults develop fluorosis?
No, fluorosis only affects developing teeth. However, adult teeth with fluorosis can be treated cosmetically.
If you’re concerned about dental fluorosis, don’t wait— contact us to discuss your options and restore your smile’s natural beauty.