Gingivitis
What Is Gingivitis?
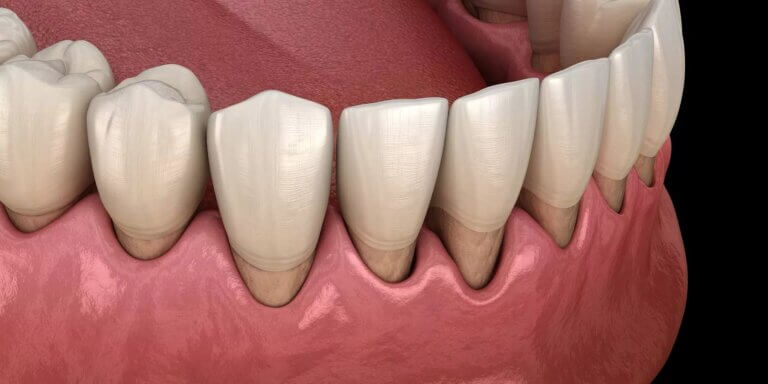
Gingivitis is a common and mild form of gum disease that causes inflammation, redness, and swelling of the gum tissues that surround and support the teeth. It is usually caused by poor oral hygiene habits that allow plaque, a sticky film of bacteria that forms on the teeth, to build up and harden into tartar.
The early symptoms of gingivitis may include bleeding gums during brushing or flossing, tender or swollen gums, and bad breath. Although gingivitis is a reversible condition, if left untreated, it can progress to a more severe form of gum disease known as periodontitis, which can lead to tooth loss..
Before you contact a Toronto dentist to examine for possible Gingivitis, there are some things you should know as a patient:
- What Is The Difference Between Gingivitis And Periodontitis?
- Why Do I Have Gingivitis?
- Signs And Symptoms Of Gingivitis
- Treatment Options For Gingivitis
- How To Prevent Gingivitis?
- Managing Gingivitis Until You Can See The Dentist
If you have questions about Gingivitis or other dental problems, please contact us for more information.
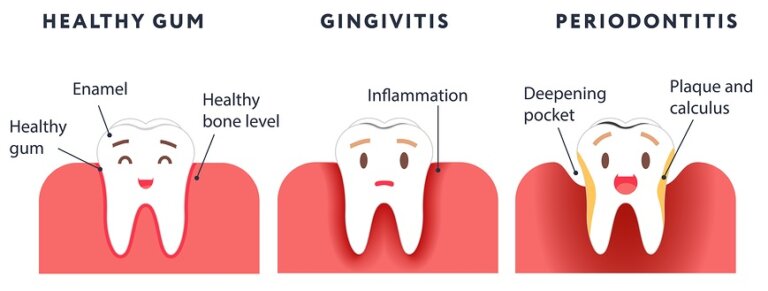
What Is The Difference Between Gingivitis And Periodontitis?
Gum disease is a progressive condition that can range from mild gum inflammation, known as gingivitis, to a more severe and chronic infection called periodontitis. Although periodontitis is a more severe form of gum disease, all cases of periodontitis begin with gingivitis.
In the early stages of gingivitis, bacteria-filled plaque builds up on the gum line, causing the gums to become swollen, inflamed, and easily prone to bleeding. However, the teeth remain firmly embedded in the bone, and there is no irreversible damage to the gums or bone at this stage. Proper oral hygiene, including brushing and flossing, can help reverse gingivitis and restore healthy gums without any permanent damage.
If left untreated, plaque can harden over time and become tartar or calculus, making it more challenging to clean teeth and gums effectively without professional help. As the disease progresses, the gums’ pathological pockets grow deeper, and more gum tissue and bone are destroyed, leading to irreversible destruction of the gum and bone supporting the teeth. The bacteria in plaque and calculus produce toxins that are harmful to the gums, and the immune system tries to fight the infection by producing enzymes. Together, these toxins and enzymes break down bone and connective tissues that hold teeth in place. As a result, teeth become loose, and tooth loss can follow. In fact, gum disease is the leading cause of tooth loss in adults.
Therefore, it’s crucial to maintain proper oral hygiene and seek professional dental care if you experience symptoms of gum disease, such as swollen or bleeding gums, bad breath, or loose teeth. Early detection and treatment of gum disease can help prevent irreversible damage and preserve your oral health. If you have further questions about Gum Disease or gingivitis, please contact us.
Why Do I Have Gingivitis?
There are several reasons why you may have gingivitis, including:
- Poor oral hygiene: Not brushing and flossing your teeth regularly can allow plaque to build up and harden into tartar, which can irritate your gums and lead to gingivitis.
- Hormonal changes: Hormonal changes during pregnancy, puberty, and menopause can make your gums more sensitive and prone to inflammation, leading to gingivitis.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as anti-seizure drugs and blood pressure medications, can cause dry mouth, which can lead to gingivitis.
- Smoking: Smoking can weaken your immune system, making it harder for your body to fight off infections such as gingivitis.
- Genetics: Some people may be genetically predisposed to developing gingivitis, even with good oral hygiene habits.
It is important to identify the underlying cause of your gingivitis and work with your dentist to develop a personalized treatment plan. In addition to improving your oral hygiene habits, treatment may include professional cleanings, medication, or changes to your medications or lifestyle habits. If you have further questions about Gingivitis, please contact us.
Signs and Symptoms of Gingivitis
The signs and symptoms of gingivitis may include:
- Red or swollen gums: Gingivitis can cause inflammation of the gums, making them appear red and swollen.
- Bleeding gums: If your gums bleed during brushing or flossing, it may be a sign of gingivitis.
- Bad breath: Gingivitis can cause persistent bad breath, despite regular brushing and flossing.
- Sensitive gums: Gingivitis can cause your gums to become more sensitive to hot and cold temperatures and touch.
If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, it is important to see your dentist as soon as possible. Gingivitis is a treatable condition, and early intervention can prevent further damage to your teeth and gums. If you have further questions about the signs and symptoms of Gingivitis, please contact us.
Treatment Options for Gingivitis
The treatment options for gingivitis may include:
- Improved oral hygiene: The first step in treating gingivitis is to improve your oral hygiene habits by brushing and flossing your teeth regularly to remove plaque and tartar buildup. Brush and floss gently around the tooth. Rinsing your mouth with mouthwash will help reduce infection, inflammation and alleviate toothache pain. You can buy any mouthwash available at your pharmacy or health foods store.
- Professional cleaning: Your dentist may recommend a professional cleaning, which involves removing plaque and tartar buildup from your teeth and gums.
- Lifestyle changes: Quitting smoking, managing stress, and eating a healthy diet can all help improve your oral and overall health.
With proper treatment and ongoing care, gingivitis can be reversed and your gums can return to a healthy state. If left untreated, however, gingivitis can progress to more advanced stages of gum disease, which can lead to tooth loss and other serious health problems. Therefore, it is important to seek prompt dental care if you suspect that you have gingivitis. If you have further questions about treatment options for Gingivitis, please contact us.
How to Prevent Gingivitis?
Preventing gingivitis requires consistent and effective oral hygiene habits, along with other healthy lifestyle choices. Here are some tips to help you prevent gingivitis:
- Brush and floss regularly: Brush your teeth at least twice a day and floss daily to remove plaque and food particles from your teeth and gums.
- Use an antimicrobial mouthwash: Rinse with an antimicrobial mouthwash to help kill bacteria and freshen your breath.
- Maintain a healthy diet: Eating a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals can help strengthen your immune system and keep your gums healthy.
- Quit smoking: Smoking weakens your immune system and makes it harder for your body to fight off infections, including gingivitis.
- Visit your dentist regularly: Regular dental check-ups and teeth cleanings can help detect and treat gingivitis early, before it progresses to more serious stages of gum disease.
By following these preventive measures, you can reduce your risk of developing gingivitis and maintain healthy gums and teeth. If you have further questions about how to prevent Gingivitis, please contact us.
Managing Gingivitis Until You Can See the Dentist
If you are experiencing symptoms of gingivitis and cannot see a dentist right away, there are several things you can do to manage the condition:
- Brush and floss regularly: Brush your teeth at least twice a day and floss daily to remove plaque and food particles from your teeth and gums. Be sure to use a soft-bristled toothbrush. Another great tool is the Waterpik waterflosser, which uses a high pressure water jet to blast away debris.
- Rinse with salt water or mouthwash: Salt water can help reduce inflammation and kill bacteria in your mouth. Mix one teaspoon of salt with eight ounces of warm water and rinse your mouth with the solution for 30 seconds, then spit it out. Alternatively you can buy mouthwash from your local pharmacy.
- Avoid smoking and alcohol: Smoking and alcohol can irritate your gums and worsen your symptoms.
- Use over-the-counter pain relievers: Over-the-counter pain medication, such as Advil (ibuprofen) or Tylenol (acetaminophen), can help relieve gum pain and reduce inflammation. Follow the instructions on the label and do not exceed the recommended dose. Unless you have a health condition that prevents you from taking either ibuprofen or acetaminophen, the absolute maximum dose that I recommend patients take for the worst dental pain is 600 mg ibuprofen combined with 1000 mg acetaminophen every 4 to 6 hours.
- Eat a healthy diet: Eating a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals can help strengthen your immune system and promote healing.
While these measures can help manage the symptoms of gingivitis, they do not replace professional dental care. It is important to see your dentist as soon as possible to receive proper treatment for gingivitis and prevent further damage to your teeth and gums. If you have further questions about managing Gingivitis, please contact us.