External Root Resorption
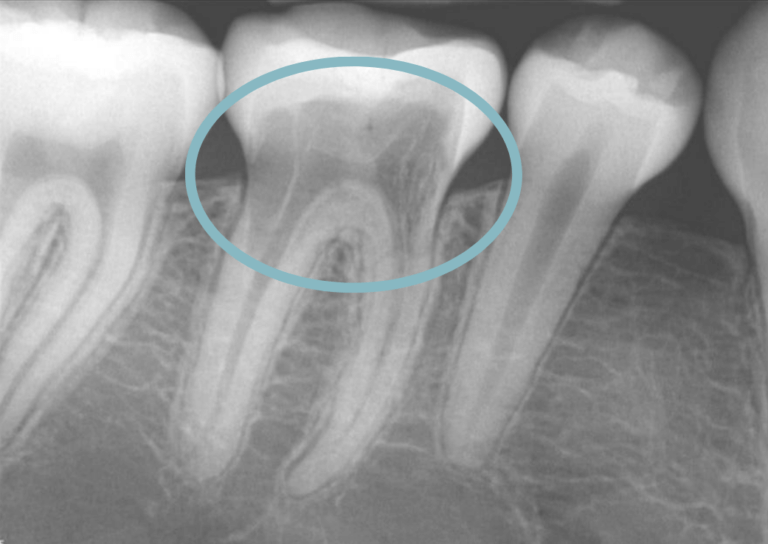
What Is External Root Resorption?
External root resorption occurs when the body’s own immune system attacks and breaks down the outer root surface of a tooth. Unlike internal root resorption that damages the root structure from the inside-out, external root resorption specifically targets the roots from the outside-in. This condition can pose challenges to dental health and, if left unaddressed, may result in discomfort and potential tooth loss.
External root resorption is not that well understood, and would appear to happen quite sporadically. It can be caused by various factors, including trauma, orthodontic treatments, infections, genetics, poor oral hygiene, and age-related changes.
Dentists may first suspect external root resorption based on symptoms like tooth sensitivity, discoloration, or mobility. Dental X-rays are crucial, as they can reveal changes in root structure, aiding in early detection. Regular dental check-ups and imaging contribute to timely diagnosis.
Before you contact a Toronto dentist to examine External Root Resorption, there are some things you should know as a patient:
- Why Do I Have External Root Resorption?
- Signs And Symptoms Of External Root Resorption
- Treatment Options For External Root Resorption
If you have questions about External Root Resorption or other dental problems, please contact us for more information.
Why Do I Have External Root Resorption?
Understanding the underlying causes of external root resorption is crucial for effective prevention and management. Several factors can contribute to this dental condition, and being aware of them empowers individuals to take proactive steps toward maintaining optimal oral health.
- Trauma to the Teeth: External root resorption may be triggered by trauma to the teeth, such as accidents or injuries. When the teeth experience forceful impacts, it can lead to a breakdown in the root surfaces, initiating the resorption process.
- Orthodontic Treatment: Individuals undergoing orthodontic treatments, like braces, may be at a higher risk of external root resorption. The pressure applied to the teeth during these procedures can contribute to the resorption process, particularly if not closely monitored by a dental professional.
- Inflammatory Conditions: Systemic inflammatory conditions, such as certain autoimmune disorders, can indirectly affect dental health. The body’s immune response may influence the tooth’s external environment, potentially triggering resorption.
- Chronic Dental Infections: Prolonged and untreated dental infections, such as abscesses, can create an environment conducive to external root resorption. The inflammation and bacterial activity compromise the integrity of the tooth structure.
- Genetic Factors: Genetic predispositions can influence an individual’s susceptibility to external root resorption. Some people may be inherently more prone to this condition due to their genetic makeup, emphasizing the importance of regular dental check-ups for early detection.
- Age-related Factors: Aging can also be a factor in external root resorption. As individuals age, changes in the dental structure and the body’s response to various stimuli may increase the likelihood of root resorption.
- Idiopathic Causes: In certain cases, external root resorption may occur without an apparent cause, leading to an idiopathic classification. While less common, these cases highlight the complexity of dental health and the need for regular check-ups.
By recognizing these potential triggers, individuals can work with their dental professionals to develop personalized strategies for prevention and early intervention, ultimately preserving the health of their teeth and mitigating the risks associated with external root resorption. For more information about External Root Resorption, please contact us.
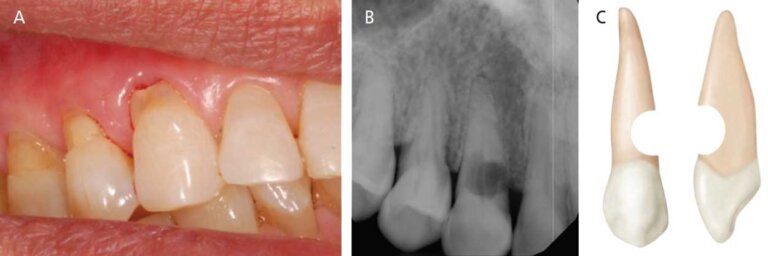
Signs And Symptoms Of External Root Resorption
Early detection of external root resorption is vital for effective treatment and preservation of dental health. Recognizing the signs and symptoms allows individuals to seek timely dental intervention, preventing further complications. Here are key indicators to be mindful of:
- Tooth Sensitivity: Experiencing heightened sensitivity to hot or cold temperatures may signal external root resorption. As the protective layers of the tooth diminish, nerve exposure can lead to increased sensitivity.
- Discoloration of the Tooth: Changes in tooth color, ranging from pinkish spots to darkening, may indicate external root resorption. This discoloration is a result of the breakdown of the tooth’s internal structure.
- Swelling and Discomfort: Localized swelling or discomfort in the gums surrounding a particular tooth can be indicative of external root resorption. Inflammation may accompany the resorption process.
- Unexplained Mobility of the Tooth: A sudden, unexplained shift in the positioning or mobility of a tooth can be a red flag for external root resorption. The resorption weakens the tooth’s attachment to the jawbone.
- Pain During Chewing or Touch: Experiencing pain while chewing or touching a specific tooth may suggest external root resorption. Pressure on the affected area can exacerbate discomfort.
- Visible Changes on Dental X-rays: Regular dental X-rays may reveal changes in the root structure, indicating external root resorption. Routine monitoring through imaging is crucial for early detection.
Being attuned to these signs and symptoms empowers individuals to seek professional dental advice promptly. If any of these indicators are noticed, scheduling a thorough examination with a dentist ensures timely intervention and a comprehensive treatment plan to address external root resorption effectively. For more information about External Root Resorption, please contact us.
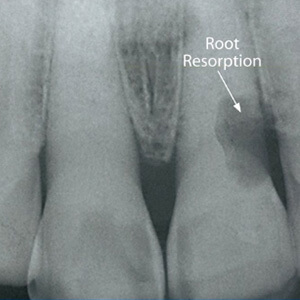
Treatment Options For External Root Resorption
Addressing external root resorption requires a tailored approach, with treatment plans designed to preserve dental health and prevent further complications. Dental professionals may recommend the following options based on the severity of the condition:
- Root Canal Therapy: For more advanced cases, especially when the internal pulp is affected, root canal therapy may be recommended. This procedure involves removing damaged tissue and sealing the tooth to prevent further resorption.
- Surgical Intervention: Severe cases may require surgical intervention. This can involve accessing the affected area to remove damaged tissue, repair the root surface, or address other contributing factors.
- Tooth Extraction and Replacement: In instances where the damage is extensive and preservation is not feasible, tooth extraction may be necessary. Dental professionals can discuss suitable replacement options, such as dental implants or bridges.
Individuals experiencing external root resorption should consult with their dentist to determine the most suitable course of action based on their specific situation. Early detection and proactive management are key to preserving dental function and aesthetics while minimizing the impact of external root resorption. For more information about External Root Resorption, please contact us.