Internal Root Resorption
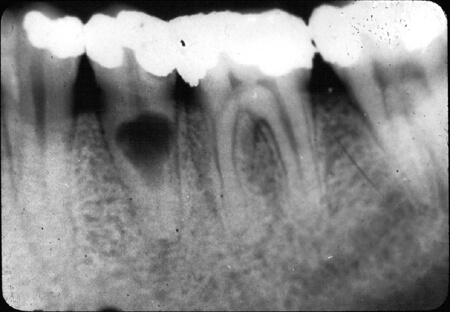
What Is Internal Root Resorption?
Internal root resorption occurs when there is an unusual breakdown of the tooth’s internal structure, particularly within the root canal. Unlike external root resorption, which affects the outer surface of the tooth, internal resorption involves changes within the tooth itself. While relatively uncommon, it demands attention due to its potential to cause discomfort and compromise the stability of the affected tooth.
Before you contact a Toronto dentist to examine Internal Root Resorption, there are some things you should know as a patient:
- Why Do I Have Internal Root Resorption?
- Signs And Symptoms Of Internal Root Resorption
- Treatment Options For Internal Root Resorption
If you have questions about Internal Root Resorption or other dental problems, please contact us for more information.
Why Do I Have Internal Root Resorption?
Understanding the root causes of internal root resorption is vital for effective prevention and management. Several factors contribute to the development of this dental condition, each shedding light on the intricate nature of oral health. Let’s explore the reasons why some individuals may experience internal root resorption:
- Trauma to the Tooth: Any traumatic incident, such as a blow to the mouth or a sports injury, can lead to internal root resorption. The impact disrupts the normal cellular activity within the tooth, triggering resorption.
- Previous Dental Procedures: Certain dental treatments, particularly those involving the root canal, may inadvertently instigate internal root resorption. Improper procedures or complications during dental work can contribute to the development of this condition.
- Chronic Dental Infections: Prolonged and untreated dental infections, such as abscesses, can create an environment conducive to internal root resorption. The inflammation and bacterial activity compromise the integrity of the tooth structure.
- Genetic Predisposition: Some individuals may have a genetic predisposition to dental issues, including internal root resorption. Genetic factors can influence the susceptibility of teeth to resorptive processes.
- Orthodontic Treatment: Orthodontic interventions, such as braces, may, in rare instances, contribute to internal root resorption. Pressure exerted during realignment can impact the tooth structure, leading to resorptive changes.
- Inflammatory Conditions: Systemic inflammatory conditions, such as certain autoimmune disorders, can indirectly affect dental health. The body’s immune response may influence the tooth’s internal environment, potentially triggering resorption.
- Idiopathic Causes: In certain cases, internal root resorption may occur without an apparent cause, leading to an idiopathic classification. While less common, these cases highlight the complexity of dental health and the need for regular check-ups.
By recognizing these potential triggers, individuals can take proactive steps to minimize the risk of internal root resorption. Regular dental check-ups, prompt treatment of infections, and mindful oral care play pivotal roles in maintaining a resilient and healthy dental structure. For more information about Internal Root Resorption, please contact us.
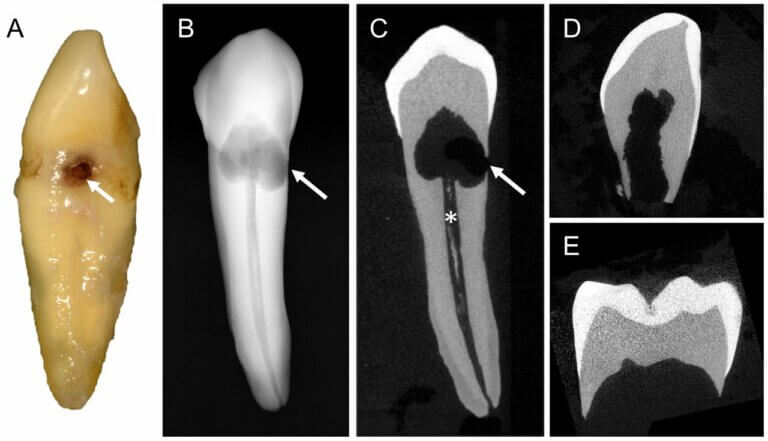
Signs And Symptoms Of Internal Root Resorption
Identifying the signs and symptoms of internal root resorption is crucial for timely intervention and effective management. While some indications may be subtle, paying attention to changes in oral health can prevent potential complications. Here are the key signals that may suggest the presence of internal root resorption:
- Tooth Discoloration: One of the earliest signs is a change in tooth color, often presenting as a pink or gray tint. This discoloration stems from the disruption of blood vessels within the tooth during the resorptive process.
- Sensitivity to Temperature: Increased sensitivity to hot or cold temperatures may indicate internal root resorption. As the tooth structure is compromised, nerve endings become more exposed, leading to heightened sensitivity.
- Swelling or Discomfort: Swelling or discomfort around the affected tooth may manifest, signaling inflammation within the root canal. This discomfort can range from mild sensitivity to persistent pain.
- Pimple on the Gums (Dental Abscess): A pimple-like swelling, known as a dental abscess, may appear on the gums near the affected tooth. This is a result of the body’s response to the infection associated with internal root resorption.
- Pain During Chewing or Touch: Experiencing pain while chewing or touching a specific tooth may suggest internal root resorption. Pressure on the affected area can exacerbate discomfort.
- Progressive Radiographic Changes: Regular dental X-rays may reveal progressive changes in the internal structure of the tooth, such as a hollow appearance or thinning of the root canal walls, indicating the presence of internal root resorption.
Being attuned to these signs allows individuals to seek prompt dental care, facilitating early diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Regular dental check-ups and open communication with your dentist are instrumental in addressing potential issues related to internal root resorption before they escalate. For more information about Internal Root Resorption, please contact us.
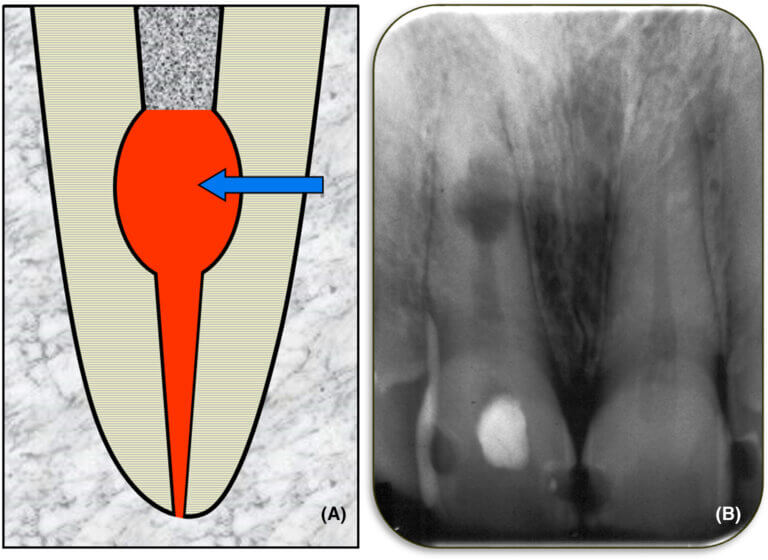
Treatment Options For Internal Root Resorption
Addressing internal root resorption involves a tailored approach that considers the severity of the condition and the patient’s overall oral health. Various treatment options aim to preserve the affected tooth and alleviate associated symptoms. Here are the key avenues for managing internal root resorption:
- Root Canal Therapy: In less severe cases, where the resorption is confined to the inner layers of the tooth, a root canal procedure may be recommended. This involves removing the affected tissue and sealing the root canal to prevent further damage.
- Apical Surgery (Apicoectomy): In situations where conventional root canal therapy may be insufficient, apical surgery may be considered. This involves removing the apex (tip) of the tooth’s root and addressing the resorption from a different angle.
- Tooth Extraction and Replacement: In more advanced cases or if the structural integrity of the tooth is compromised, extraction may be necessary. Tooth replacement options, such as dental implants or bridges, can then be explored to restore function and aesthetics.
It’s essential to consult with a qualified dentist to determine the most suitable course of action based on individual circumstances. Early intervention and a proactive approach to oral health contribute significantly to the successful management of internal root resorption, preserving dental function and aesthetics. For more information about Internal Root Resorption, please contact us.