Dental Sinus Infection
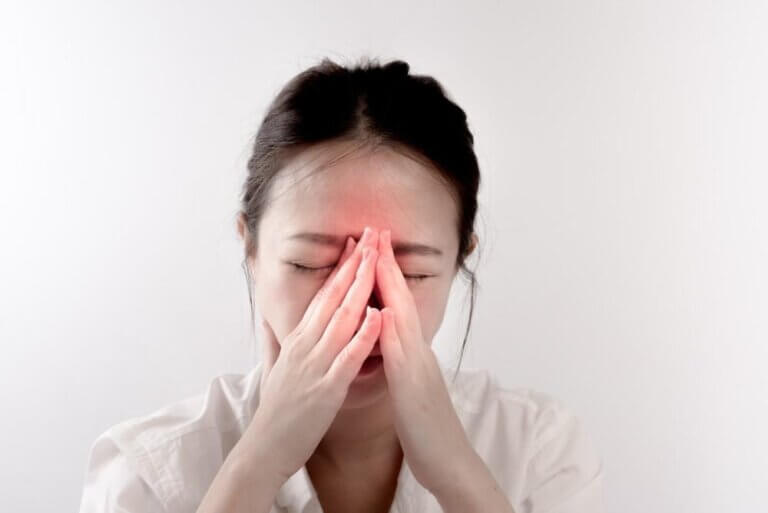

What Is A Dental Sinus Infection?
Sinus infection, also known as sinusitis, is a common condition that affects the sinuses – the air-filled cavities in the skull that are located behind the forehead, cheeks, and eyes. The sinuses produce mucus, which helps to moisten and clean the nasal passages, but when the sinuses become inflamed or infected, this can cause a buildup of mucus that leads to symptoms such as facial pain, pressure, congestion, and headache.
While sinusitis is typically thought of as a respiratory problem, it can have a dental origin. This is because the maxillary sinuses – the largest of the four pairs of sinuses – are located above the upper molars and premolars. Dental infections or procedures can sometimes lead to sinus infections if bacteria spread from the mouth to the sinuses. When the maxillary sinuses become infected or inflamed, this can cause referred pain to the teeth and jaw. As such, it is important for dentists and patients to be aware of the potential connection between sinus infections and dental issues. Before you contact a Toronto dentist to examine a potential Sinus Infection of dental origin, there are some things you should know as a patient:
- Why Do I Have A Sinus Infection?
- Signs and Symptoms of A Dental Sinus Infection
- How To Diagnose Dental Sinus Infection
- Treatment Options for Dental Sinus Infection
- How to Prevent Dental Sinus Infection
- Managing Dental Sinus Infection Until You Can See The Dentist
If you have questions about Sinus Infection or other dental problems, please contact us for more information.
Why Do I Have A Sinus Infection?
There are several factors that can contribute to the development of a sinus infection, including:
- Dental infections: Bacteria from dental infections, such as cavities or gum disease, can spread to the sinuses and cause an infection.
- Sinus barotrauma: Changes in air pressure during dental procedures or air travel can cause barotrauma to the sinuses, leading to inflammation and infection.
- Allergies: Allergic reactions to substances such as pollen, dust mites, or pet dander can cause inflammation in the sinuses, leading to a sinus infection.
- Dental procedures: Certain dental procedures, such as tooth extractions or dental implants, can cause sinus perforations, which can lead to an infection.
- Smoking: Smoking can irritate the sinuses and weaken the immune system, making it easier for infections to develop.
- Nasal polyps: Nasal polyps are small growths in the sinuses or nasal passages that can block the sinuses and lead to infection.
- Weak immune system: A weakened immune system due to factors such as illness or medication can make it easier for infections to develop.
It’s important to note that these factors can also interact with each other, making it more likely for a sinus infection to occur. If you have further questions whether the sinus pain you are experiencing is due to a dental problem, please contact us.
Signs and Symptoms of A Dental Sinus Infection
Some of the signs and symptoms of a dental sinus infection include:
- Pain and pressure in the sinuses: You may experience pain or pressure in the area around your sinuses, which can be accompanied by a headache.
- Tooth pain: Dental sinus infections can cause tooth pain or sensitivity, especially in the upper back teeth.
- Headache: Sinus headaches often cause pain in the forehead or around the eyes.
- Swelling and tenderness: You may experience swelling and tenderness around your sinuses, which can be painful to the touch.
- Nasal congestion: A dental sinus infection can cause nasal congestion or a runny nose.
- Fatigue: You may feel tired or fatigued due to the infection.
- Fever: A fever may be present if the sinus infection is caused by a bacterial infection.
- Bad breath: This may be caused by the buildup of mucus in the sinuses.
- Ear pain: Sinus infections can cause referred pain to the ears, leading to ear pain or pressure.
If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s important to see your dentist for an evaluation. Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent the infection from worsening and causing more severe symptoms. If you have further questions about signs and symptoms of Dental Sinus Infection, please contact us.
How To Diagnose Dental Sinus Infection
If you suspect you have a dental sinus infection, your dentist may perform the following tests to diagnose the infection:
- Intra-oral examination: An intra-oral examination involves a thorough examination of the affected tooth and surrounding gums to look for signs of infection, such as redness, swelling, or discharge. The dentist will determine the location and severity of the dental sinus infeciton and whether additional tests, such as X-rays, are necessary.
- Dental X-rays: Conventional 2-dimensional dental x-ray images, such as periapical x-rays or panoramic x-rays, can show signs of dental infection, such as tooth decay or abscess.
- CBCT scan: A CBCT scan (Cone Beam Computed Tomography) is a specialized type of X-ray imaging that produces detailed three-dimensional images of the teeth, jaw, and surrounding structures. It can provide a more detailed image of the sinuses and help to identify any signs of infection or inflammation.
Your dentist may also review your medical history and ask about your symptoms to help make a diagnosis. Once a diagnosis has been made, your dentist can recommend an appropriate treatment plan. If you have further questions about how to diagnose a Dental Sinus Infection, please contact us.
Treatment Options for Dental Sinus Infection
There are several treatment options available for dental sinus infection, depending on the severity of the infection:
- Antibiotics: Antibiotics are often prescribed to treat bacterial infections that cause dental sinus infections.
- Tooth removal: If a decayed or infected tooth is causing the sinus infection, tooth extraction may be necessary to eliminate the source of the infection. Sometimes this is necessary when the tooth is too damaged to be repaired. Tooth replacement options include dental implants, dental bridges and dentures.
- Root canal treatment: Root canal treatment is a dental procedure performed to save a damaged or infected tooth. It involves removing the damaged or infected pulp (soft tissue inside the tooth) and cleaning the inside of the tooth before filling and sealing it. This procedure helps to prevent further decay or infection and allows the tooth to be saved rather than extracted. After root canal therapy, the tooth must be restored with a permanent filling and dental crown.
- Sinus surgery: In severe cases, sinus surgery may be required to remove infected or damaged tissue and improve drainage. This is often done with an ENT specialist.
Your dentist will work with you to determine the best treatment plan for your individual case. It’s important to follow your dentist’s instructions and complete the full course of treatment to ensure that the infection is fully resolved. If you have further questions about treatment options for a Sinus Infection of dental origin, please contact us.
How to Prevent Dental Sinus Infection
Preventing sinus infections can involve a combination of good dental hygiene and healthy habits, including:
- Practice good dental hygiene: This includes brushing twice a day and flossing daily. The Waterpik waterflosser is also a terrific adjunctive tool to keep your teeth clean and prevent dental infections that can spread to the sinuses.
- Avoid smoking: Smoking cigarettes can irritate the sinus soft tissue lining and increase the risk of sinus infections or make dental sinus infections feel worse.
- Manage allergies: If you have allergies, work with your healthcare provider to manage them effectively to reduce the risk of sinus infections. Prescription nasal sprays, such as corticosteroids, can help to reduce inflammation in the sinuses and improve breathing.
- Avoid nasal irritants: Avoid exposure to pollutants and chemicals that can irritate the sinuses, such as strong perfumes or cleaning products.
- Regular dental visits: Regular dental visits can help to identify and treat dental problems before they lead to sinus infections.
By following these healthy habits and working with your healthcare provider and dentist to manage dental and sinus issues, you can reduce your risk of developing a sinus infection. If you have further questions about how to prevent dental problems that can lead to a Sinus Infection, please contact us.
Managing Dental Sinus Infection Until You Can See The Dentist
If you’re experiencing symptoms of a dental sinus infection, it’s important to see your dentist as soon as possible for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. However, in the meantime, there are some steps you can take to manage your symptoms:
- Use Over-the-Counter Pain Medication: Over-the-counter pain medication, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen, can help relieve tooth pain or sensitivity from a dental infection. You are also welcome to use over the counter pain relievers such as ibuprofen (Advil) or acetaminophen (Tylenol). Ask your dentist what dosage is right for you, but if you do not have a pre-existing medical condition of allergies, 1000mg acetaminophen (Tylenol) with 600mg ibuprofen (Advil) every 4-6 hours or as needed is a very powerful combination.
- Practice good oral hygiene: Keeping your teeth as clean as possible can help prevent dental sinus infections from getting worse and alleviate some of the pain or sensitivity. Brush and floss gently around the tooth. Rinsing your mouth with warm salt water or mouthwash can help reduce infection, inflammation and alleviate toothache pain. You can buy any mouthwash available at your pharmacy or health foods store. Alternatively, you can mix a teaspoon of salt in a cup of warm water and swish the solution around your mouth for about 30 seconds before spitting it out.
- Warm compresses: Applying a warm compress to the affected area can help to reduce pain and inflammation.
- Nasal decongestants: Over-the-counter nasal decongestants can help to reduce swelling in the sinuses and relieve congestion.
- Steam inhalation: Inhaling steam from a hot shower or a bowl of hot water can help to moisten the sinuses and relieve congestion.
- Use a humidifier: Adding moisture to the air can help to keep the sinuses moist and reduce the risk of infections.
- Saline nasal irrigation: This involves flushing the nasal passages with a saline solution to help clear out mucus and reduce inflammation.
- Hydration: Drinking plenty of water and other fluids can help to thin mucus and promote drainage of the sinuses.
It’s important to note that while these steps can help to manage your symptoms, they may not fully address the underlying dental or sinus issue. Therefore, it’s important to seek treatment from a healthcare provider or dentist as soon as possible. If you have further questions about how to manage a dental Sinus Infection, please contact us.