Missing Tooth
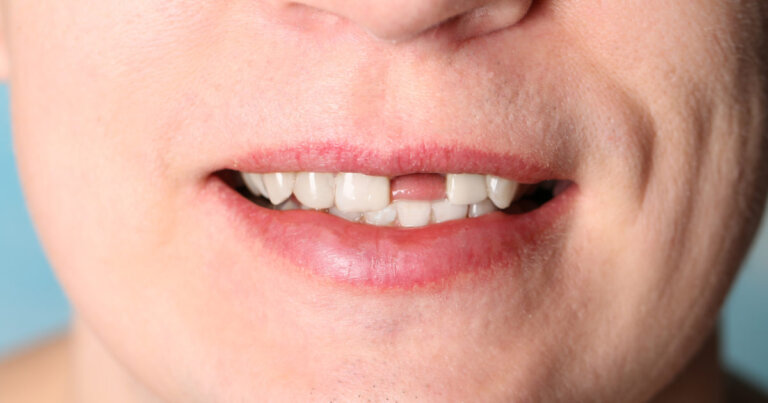

What Is A Missing Tooth?
A Missing Tooth refers to a condition where a tooth is no longer present in the mouth, either due to extraction or loss from injury, tooth decay or gum disease. A missing tooth can significantly impact one’s oral health and quality of life, affecting the ability to chew food, speak clearly, and even impacting your facial esthetics. It is essential to understand the causes, consequences, and treatment options for a missing tooth to maintain good oral health and overall well-being.
Before you contact a Toronto dentist to examine ways of replacing a missing tooth, there are some things you should know as a patient:
- Why Do I Have A Missing Tooth?
- Signs And Symptoms Of A Missing Tooth
- Treatment Options For A Missing Tooth
- How To Prevent A Missing Tooth
- Managing A Missing Tooth Until You Can See The Dentist
If you have questions about A Missing Tooth or other dental problems, please contact us for more information.
Why Do I Have A Missing Tooth?
There are various reasons why you might have a missing tooth. Some common causes include:
- Dental decay: Tooth decay is caused by the interaction of bacteria in dental plaque and sugars or carbohydrates from the food we eat, which produces acid that erodes the tooth enamel over time. Poor oral hygiene, frequent snacking, and certain medical conditions and medications can also contribute to tooth decay. When cavities are left untreated, they can cause severe damage to the tooth, leading to tooth loss.
- Gum disease: Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is typically caused by poor oral hygiene, which allows dental plaque to accumulate on and around the teeth and gums. The bacteria in plaque produce toxins that irritate the gum tissue and cause inflammation, leading to gingivitis. If left untreated, gingivitis can progress to periodontitis, which can cause destruction of the gums and bones supporting teeth. In turn, this leads to tooth loss.
- Trauma or injury: A sudden impact to the face or mouth, such as a fall, sports injury, or car accident, can knock out a tooth from its socket, make it become loose, or cause damaging fractures to the tooth crown. If the damage is severe, the tooth cannot be saved and will have to be removed.
- Congenitally missing teeth: Congenitally missing teeth are teeth that fail to develop due to genetic factors. This condition is relatively common and can affect up to 20% of the population. Congenitally missing teeth can affect any teeth, but the most commonly missing teeth are the wisdom teeth, second premolars, and lateral incisors. In some cases, congenitally missing teeth may not cause any significant issues, but in other cases, missing teeth can affect speech, eating, and the appearance of the smile. Treatment options for congenitally missing teeth may include orthodontic treatment, dental implants, or other restorative dentistry procedures like dental bridges.
- Age: The wear and tear on teeth over time can lead to decay, cracks, and other damage that can cause tooth loss. Additionally, gum disease becomes more common as we age, and can progress more rapidly if left untreated. Other factors that can contribute to tooth loss as we age include changes in saliva production, which can affect the mouth’s ability to neutralize acid and fight bacteria, and changes in bone density that can weaken the jawbone and affect tooth stability. Finally, age-related health conditions or medications can also increase the risk of tooth loss.
- Genetics: Some people may have a genetic predisposition to tooth loss or have conditions that increase the risk of dental problems. Examples of genetic disorders that contribute to tooth loss include: Amelogenesis Imperfecta, Dentinogenesis Imperfecta, Ectodermal Dysplasia, and Papillon-Lefevre Syndrome.
- Smoking: Tobacco use can lead to gum disease, which is a leading cause of tooth loss. Additionally, smoking will cause delayed healing of the gums and bones, dry mouth and reduced bone density.
It is essential to identify the underlying cause of your missing tooth to prevent further tooth loss and maintain good oral health. Your dentist can help you determine the cause of your tooth loss and recommend appropriate treatment options. If you have further questions about A Missing Tooth, please contact us.
Signs And Symptoms Of A Missing Tooth
Losing a tooth can cause a range of signs and symptoms, including:
- Visible gap or space: A visible gap or space in your smile where the missing tooth used to be.
- Difficulty biting and chewing: Difficulty in biting and chewing food due to the reduced number of occluding teeth, or spaced between your teeth that will reduce chewing efficiency.
- Speech changes: Difficulty in speaking clearly, especially when pronouncing certain words or sounds.
- Shifting of surrounding teeth: Teeth adjacent to the missing tooth may shift or move into the gap, causing misalignment or bite problems.
- Bone loss: Tooth loss can cause bone loss in the jaw, leading to changes in facial appearance and denture instability.
- Self-esteem issues: Missing teeth can affect your self-esteem and confidence, leading to social anxiety and avoidance of social situations.
If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, it is essential to consult your dentist promptly. Your dentist can examine your mouth and provide appropriate treatment options to restore your smile and oral health. If you have further questions about signs and symptoms of A Missing Tooth, please contact us.
Treatment Options For A Missing Tooth
There are several treatment options for a missing tooth, depending on the cause, location, and severity of tooth loss. Some common treatment options include:
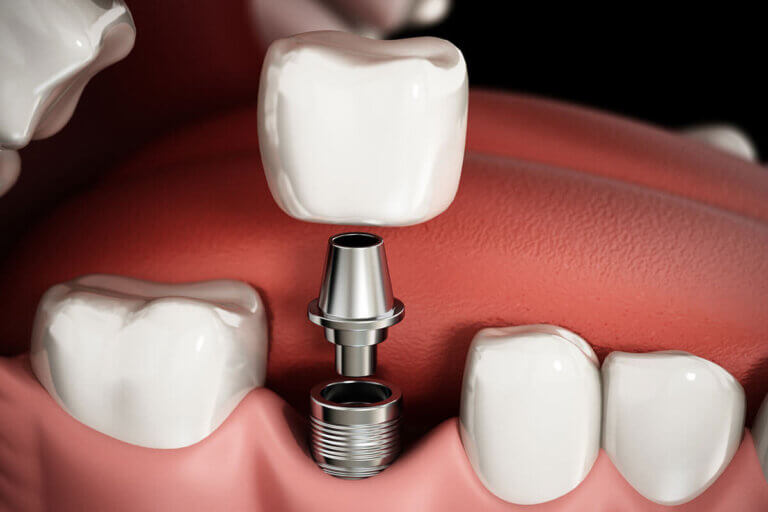
- Dental implants: A dental implant is a surgically placed artificial tooth root that supports a replacement tooth or bridge. Implants provide a durable, long-lasting solution that looks and functions like a natural tooth.
- Dental bridges: A bridge is a dental appliance that uses adjacent teeth to support a replacement tooth. Bridges are a popular option for those who cannot undergo implant surgery.
- Dentures: Dentures are removable appliances that replace one or more missing teeth. They can be partial, replacing only a few teeth, or full, replacing all the teeth in one or both jaws.
- Orthodontic treatment: Orthodontic treatment may be necessary to correct misalignment or shifting of teeth caused by a missing tooth. The dentist or orthodontist rendering orthodontic treatment can either open up the space for a replacement tooth such as a dental implant, or close the space entirely.
Your dentist can help you determine the best treatment option for your specific needs and budget. In some cases, a combination of treatments may be necessary to achieve the desired results. If you have further questions about treatment options for A Missing Tooth, please contact us.
How To Prevent A Missing Tooth
Preventing tooth loss requires consistent dental care and healthy oral habits. Here are some tips for preventing a missing tooth:
- Brush twice a day: Brush your teeth twice a day with fluoride toothpaste to remove plaque and prevent tooth decay.
- Floss daily: Floss at least once a day to remove food particles and plaque from between your teeth and under the gum line.
- Eat a healthy diet: Eat a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals, especially calcium and vitamin D, to maintain strong and healthy teeth.
- Avoid tobacco products: Smoking and tobacco use can increase the risk of gum disease and tooth loss.
- Wear a mouthguard: Wear a mouthguard during sports or other physical activities to protect your teeth from injury.
- Visit the dentist regularly: Visit your dentist at least twice a year for regular check-ups and cleanings to detect and treat dental problems early.
Following these preventive measures can help reduce the risk of tooth loss and maintain good oral health. If you have further questions about signs and symptoms of A Missing Tooth, please contact us.
Managing A Missing Tooth Until You Can See The Dentist
If you experience a missing tooth before your dental appointment, there are a few things you can do to manage the situation temporarily:
- Apply gauze: If the missing tooth is bleeding, apply gauze to the area and apply gentle pressure to stop the bleeding.
- Practice good oral hygiene: Keeping the area around the missing tooth as clean as possible can help alleviate tooth pain. Brush and floss gently around the area of the missing tooth. Rinsing your mouth with warm salt water or mouthwash can help reduce infection, inflammation and alleviate toothache pain. You can buy any mouthwash available at your pharmacy or health foods store. Alternatively, you can mix a teaspoon of salt in a cup of warm water and swish the solution around your mouth for about 30 seconds before spitting it out.
- Avoid hard or sticky foods: Avoid hard or sticky foods that can dislodge a loose tooth or cause further damage to the area. Favor using the other side of the mouth to eat and chew so as to not damage the area of the missing tooth.
- Use dental wax: If you have a sharp or jagged edge from a broken tooth, apply dental wax to the area to protect your tongue and cheeks from cuts or bruises.
It is essential to see your dentist as soon as possible to avoid further damage or complications. If you have further questions about managing A Missing Tooth, please contact us.